Unveiling The Science Behind Daylight Gains: A Comprehensive Guide
Mar 26 2025
As the seasons change, one of the most intriguing natural phenomena is the gradual increase in daylight hours during spring and early summer. If you've ever wondered how much daylight is gained each day, this article dives deep into the science, patterns, and factors influencing daylight changes. Understanding the Earth's axial tilt and orbital motion provides clarity on why some regions experience dramatic daylight shifts while others see minimal changes. This knowledge is not only fascinating but also practical for planning outdoor activities, energy consumption, and even mental well-being.
Daylight patterns are influenced by the Earth's position relative to the Sun, creating variations that depend on geographic location and time of year. The concept of daylight gain is particularly noticeable during the spring equinox, when the Sun's path shifts northward, leading to longer days in the Northern Hemisphere. This phenomenon has been studied for centuries, with ancient cultures devising calendars and observatories to track these changes. Modern science adds precision to these observations, offering tools to predict how much daylight is gained each day with remarkable accuracy.
Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a gardener, or simply someone curious about the world around you, understanding daylight patterns enriches your appreciation of the natural rhythms governing our planet. This article explores the science behind daylight changes, explains regional variations, and addresses common misconceptions. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how much daylight is gained each day and how it impacts daily life.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Ppd Test Philadelphia Everything You Need To Know
Table of Contents
- How Much Daylight is Gained Each Day?
- What Causes Daylight Changes?
- Regional Variations in Daylight Gains
- How Does Latitude Affect Daylight?
- Understanding the Earth's Axial Tilt
- How Much Daylight is Gained During Spring?
- Daylight Patterns and Seasonal Shifts
- Measuring Daylight Gains
- Impact of Daylight on Daily Life
- Common Misconceptions About Daylight
How Much Daylight is Gained Each Day?
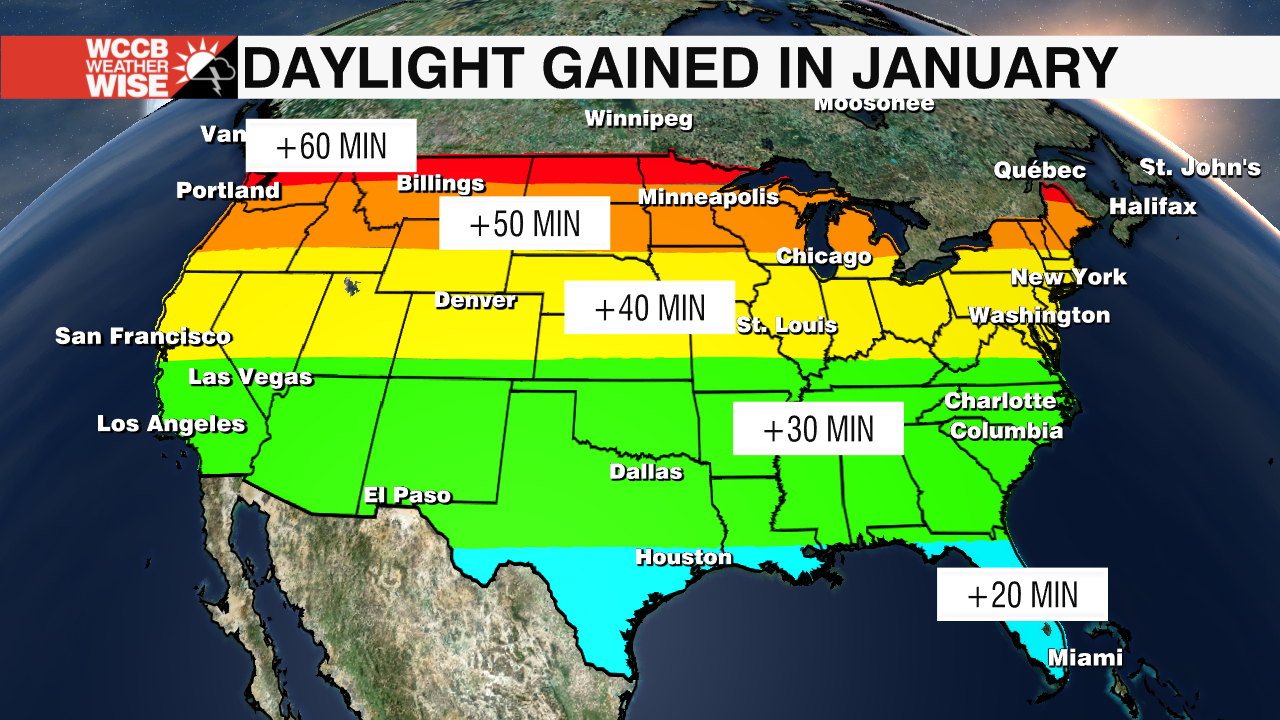
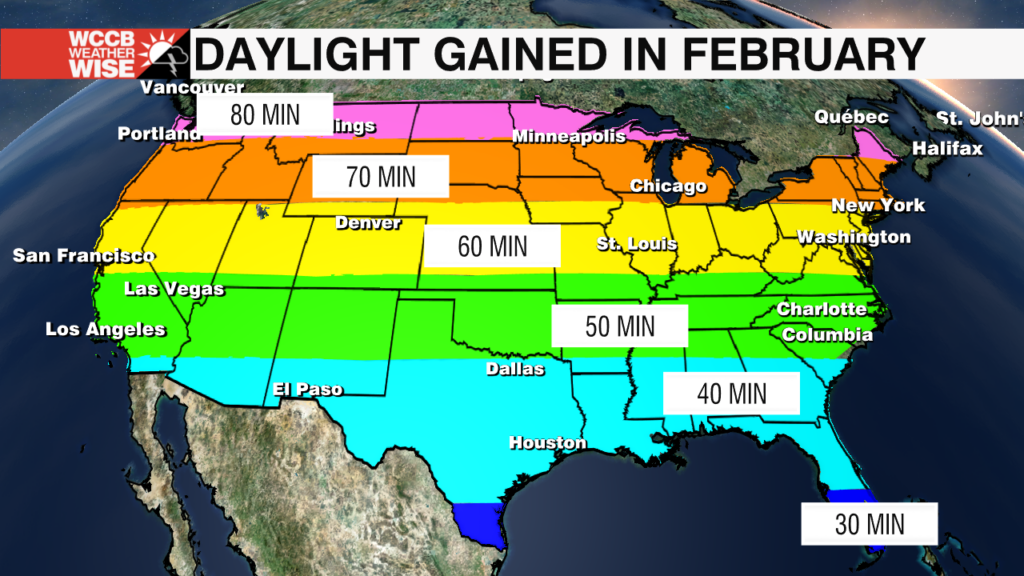
One of the most common questions about daylight changes is, "How much daylight is gained each day?" The answer depends on several factors, including your geographic location and the time of year. During the spring equinox, the Northern Hemisphere begins to receive more sunlight as the Earth's tilt shifts the Sun's direct rays northward. In regions closer to the equator, the increase in daylight is relatively small, often just a few minutes per day. However, in higher latitudes, such as northern Europe or Canada, the gains can be much more significant, sometimes exceeding two minutes per day.
Understanding these patterns requires examining the Earth's axial tilt and its orbit around the Sun. The tilt determines which hemisphere receives more direct sunlight at different times of the year, while the elliptical shape of the Earth's orbit influences the speed of these changes. For example, the rate of daylight gain tends to be faster near the equinoxes and slower near the solstices. This variability creates unique experiences for people living in different parts of the world.
What Causes Daylight Changes?
Daylight changes are primarily driven by the Earth's axial tilt and its revolution around the Sun. The axial tilt, approximately 23.5 degrees, causes the Sun's rays to strike the Earth at varying angles throughout the year. During the summer solstice, the hemisphere tilted toward the Sun experiences the longest day of the year, while the opposite hemisphere experiences the shortest. As the Earth continues its orbit, the angle of sunlight gradually shifts, leading to the gradual increase or decrease in daylight hours.
How Does Latitude Affect Daylight?
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining how much daylight is gained each day. Regions closer to the equator experience relatively stable daylight patterns throughout the year, with only minor variations between the longest and shortest days. In contrast, areas closer to the poles experience extreme seasonal changes. During the summer, these regions can enjoy nearly 24 hours of daylight, while in winter, they may experience extended periods of darkness. This phenomenon, known as the "midnight sun" or "polar night," highlights the dramatic impact of latitude on daylight patterns.
Regional Variations in Daylight Gains
Daylight gains vary significantly across different regions of the world. For example, someone living in Seattle, Washington, will notice a much more pronounced increase in daylight during spring compared to someone in Miami, Florida. This difference is due to Seattle's higher latitude, which amplifies the effects of the Earth's axial tilt. In contrast, Miami's proximity to the equator results in more consistent daylight patterns throughout the year. Understanding these regional variations helps explain why people in different locations may have different perceptions of how much daylight is gained each day.
Understanding the Earth's Axial Tilt
The Earth's axial tilt is the primary driver of seasonal changes and daylight patterns. Without this tilt, the planet would experience uniform daylight throughout the year, with no distinct seasons. The tilt causes the Sun's rays to strike the Earth's surface at varying angles, creating differences in temperature and daylight duration. During the spring and summer, the Northern Hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, resulting in longer days and warmer temperatures. In autumn and winter, the tilt shifts away, leading to shorter days and cooler weather.
Read also:Krista Miller Born Unveiling The Journey Of A Remarkable Personality
How Much Daylight is Gained During Spring?
Spring is the season when daylight gains are most noticeable, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. As the Earth moves toward the spring equinox, the rate of daylight increase accelerates, often peaking just before the equinox. During this period, regions at higher latitudes can gain as much as two minutes of daylight per day, while equatorial regions may see gains of only a few seconds. This rapid increase in daylight is a welcome change for many, signaling the end of winter and the start of longer, brighter days.
Daylight Patterns and Seasonal Shifts
Daylight patterns follow predictable seasonal shifts, influenced by the Earth's position relative to the Sun. These shifts create distinct patterns in different hemispheres, with the Northern Hemisphere experiencing longer days during spring and summer and shorter days during autumn and winter. The Southern Hemisphere experiences the opposite pattern, with its seasons occurring six months out of sync with the Northern Hemisphere. This symmetry highlights the interconnectedness of global daylight patterns and the universal impact of the Earth's axial tilt.
Measuring Daylight Gains
Measuring how much daylight is gained each day involves tracking the duration of sunlight over time. This can be done using tools such as sundials, photometers, or even smartphone apps designed for tracking daylight hours. Scientists also use advanced models to predict daylight patterns based on geographic location and time of year. These models take into account factors such as latitude, altitude, and atmospheric conditions to provide precise estimates of daily daylight gains.
Impact of Daylight on Daily Life
The increase in daylight during spring and summer has a profound impact on daily life, influencing everything from mood and energy levels to work schedules and recreational activities. Longer days provide more time for outdoor activities, while shorter days in winter encourage indoor pursuits. Studies have shown that increased exposure to natural light can improve mental health, boost productivity, and enhance overall well-being. Understanding how much daylight is gained each day helps individuals plan their lives more effectively, taking advantage of the benefits that longer days bring.
Common Misconceptions About Daylight
Despite widespread interest in daylight patterns, several misconceptions persist. One common myth is that daylight gains occur at a constant rate throughout the year. In reality, the rate of change varies depending on the time of year and geographic location. Another misconception is that daylight patterns are identical in both hemispheres, ignoring the six-month phase difference between Northern and Southern Hemisphere seasons. By addressing these misconceptions, we can gain a clearer understanding of how much daylight is gained each day and why these changes matter.
Why Does Daylight Matter?
Daylight is more than just a natural phenomenon; it plays a vital role in shaping human experience and the natural world. From regulating circadian rhythms to influencing plant growth, daylight impacts nearly every aspect of life on Earth. As we continue to study and understand these patterns, we gain valuable insights into the intricate relationship between our planet and its star. Whether you're tracking how much daylight is gained each day or simply enjoying the benefits of longer days, the science of daylight offers endless opportunities for exploration and discovery.
In conclusion, understanding how much daylight is gained each day requires a combination of scientific knowledge, geographic awareness, and appreciation for the natural rhythms governing our planet. By exploring the factors that influence daylight patterns and addressing common misconceptions, we can deepen our connection to the world around us and make the most of the precious hours of sunlight available to us each day.